
Survivorship bias when failure gets Ness Labs
Survivorship bias - lessons from World War Two aircraft I don't know about you, but I spent quite a bit of my Easter fighting in 1940 Western Europe. My teenage daughter, Zoe, playing the Axis powers, made quick work of France. England was standing alone as the German navy massed in the channel.

Survivor bias and the mistake of stability Harro
During WWII, countries had to solve many mathematical and strategic tasks in order to succeed during the war. One of those difficult assignments was to find ways of improving aircraft so they would be more resistant to enemy fire. While statisticians struggled to find the best way to protect the planes, one man named Abraham Wald had a genius idea that is implemented in many places to this day.
Survivorship Bias Aseem Shrey
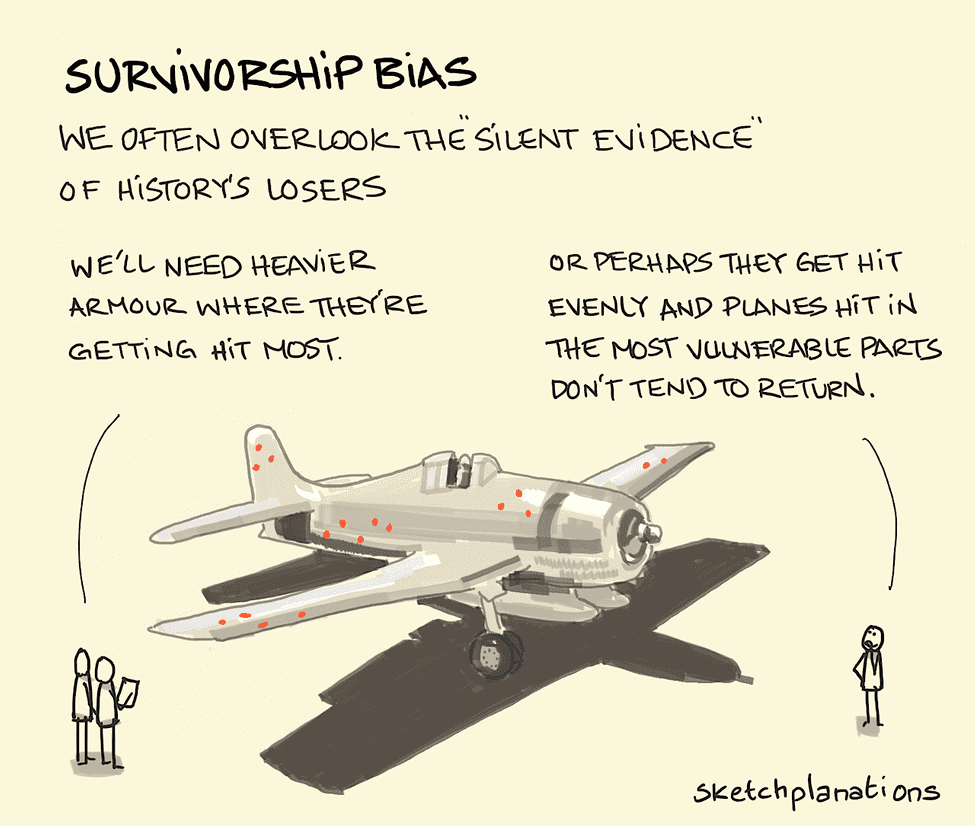
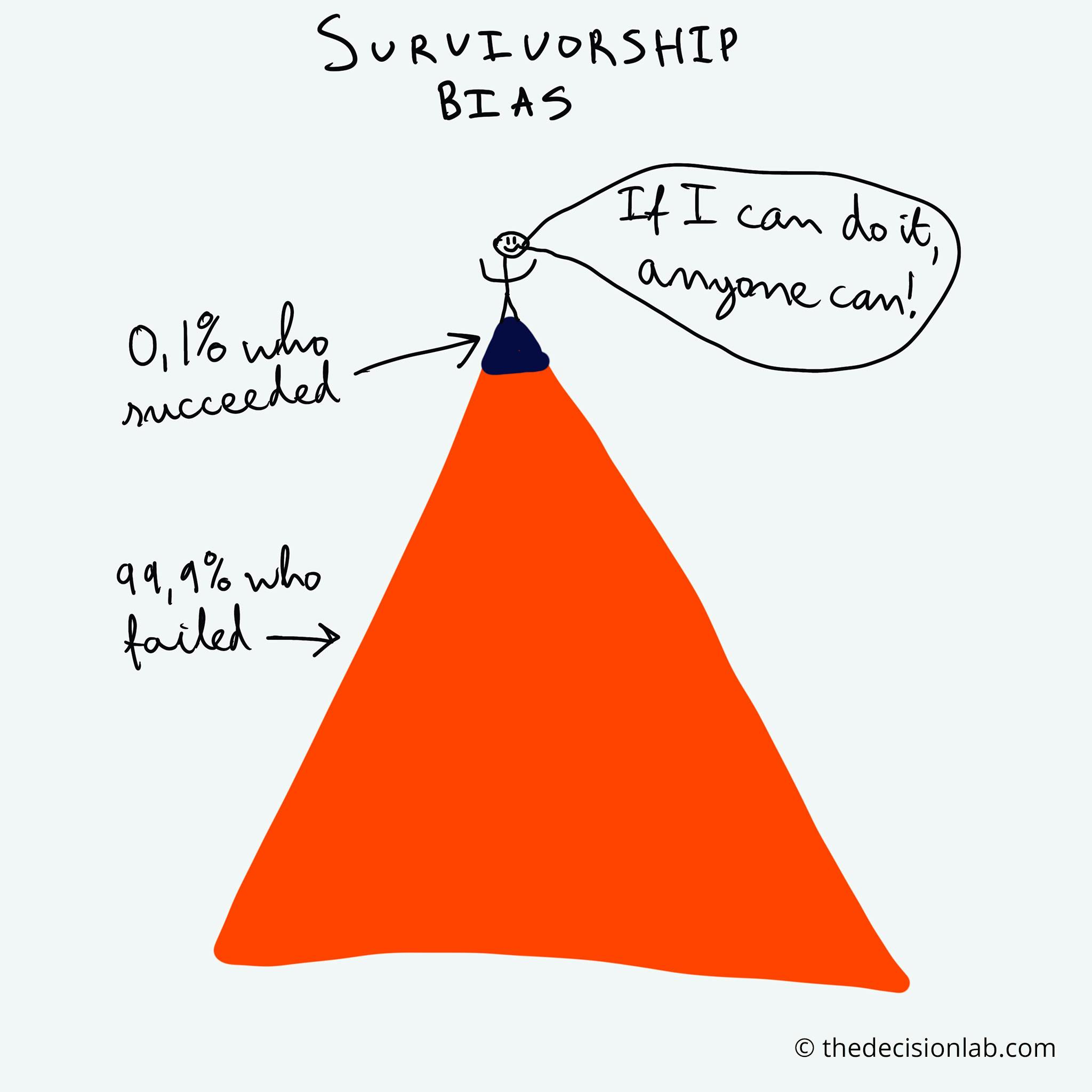
Survivorship bias (or survivor bias) is a cognitive fallacy in which, when looking at a given group, you focus only on examples of successful individuals (the "survivors") in the selection process rather than the group as a whole (including the "non-survivors").

Survivorship Bias Story of failures Shadnan Mahmud's
Survivorship Bias - Abraham Wald and the WWII Airplanes by Jerry Silfwer Survivorship bias is a tricky phenomenon. During World War II, the Allies studied Nazi damage to their airplanes. Their study resulted in this dotted illustration: This airplane seems to have some sort of condition.

WW2 Engineers Made The Mistake Of Only Analyzing Surviving Planes Not
Survivorship bias is a type of selection bias where the results, or survivors, of a particular outcome are disproportionately evaluated. Those who "failed", or did not survive, might even be ignored. Focusing on the survivors can result in a false, or incorrect, estimate of probability.

Level Up Fun Blog Survivorship Bias
Survivorship bias is the tendency on concentrating all the attention on the companies that were successful while forgetting about all the companies that failed in that period. If this concept is true, and it works applied to the case of the plane's damage, you may be wondering why I told you it was a myth.
7 Lessons on Survivorship Bias that Will Help You Make Better Decisions
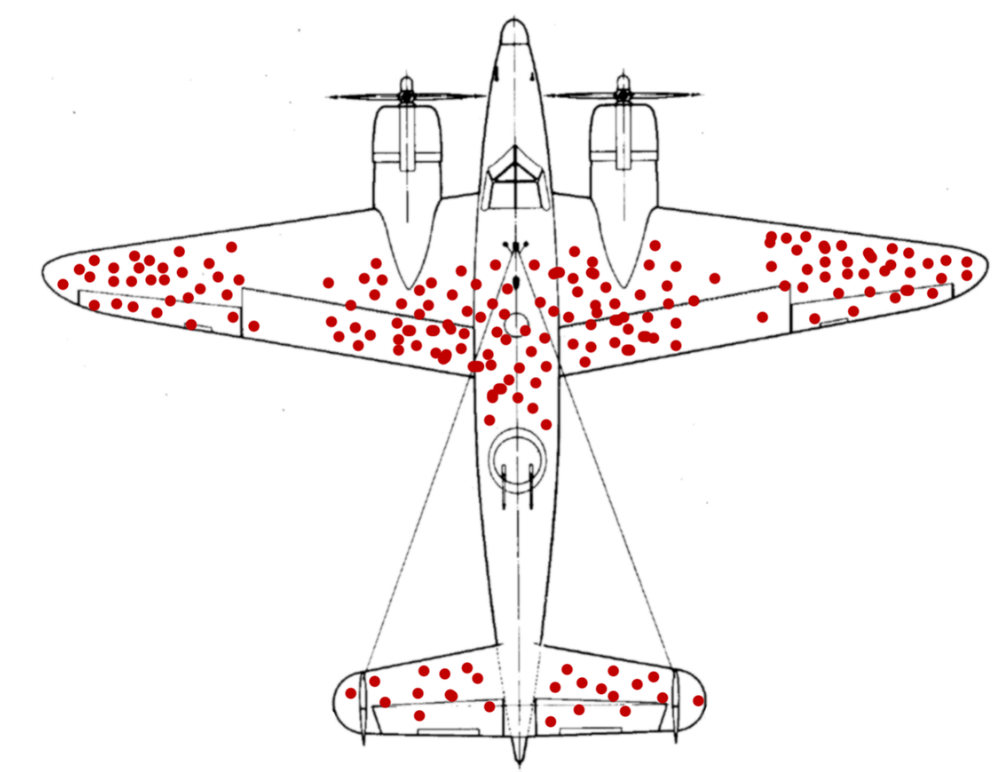
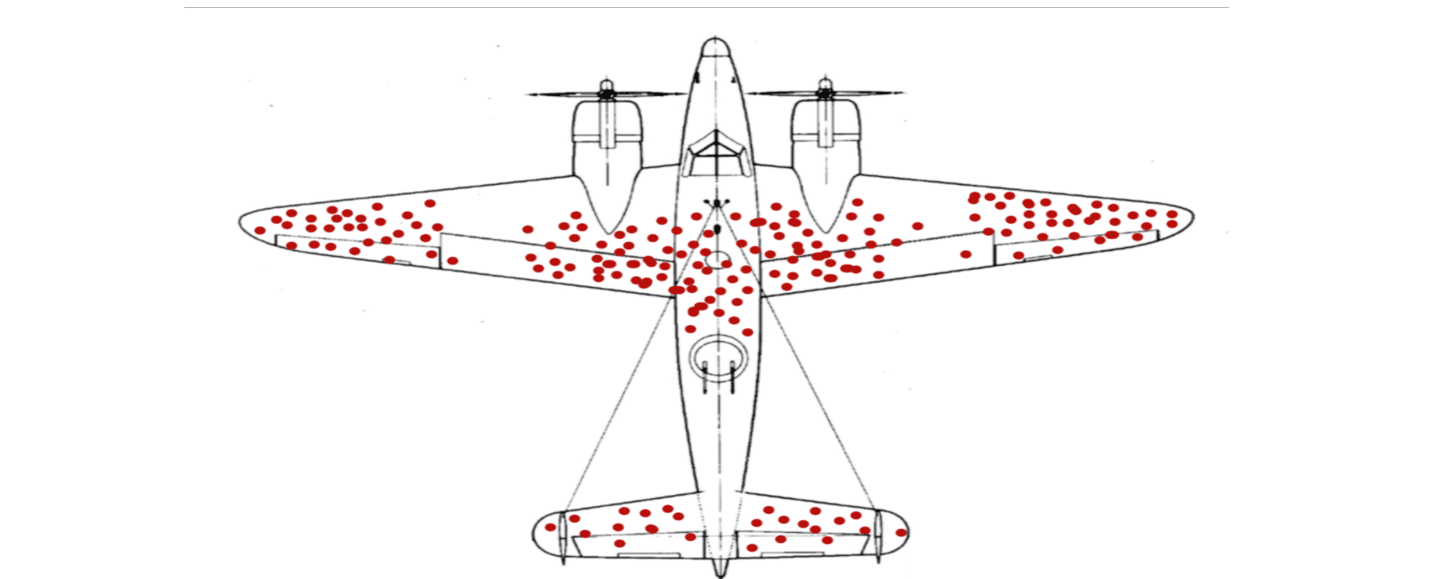
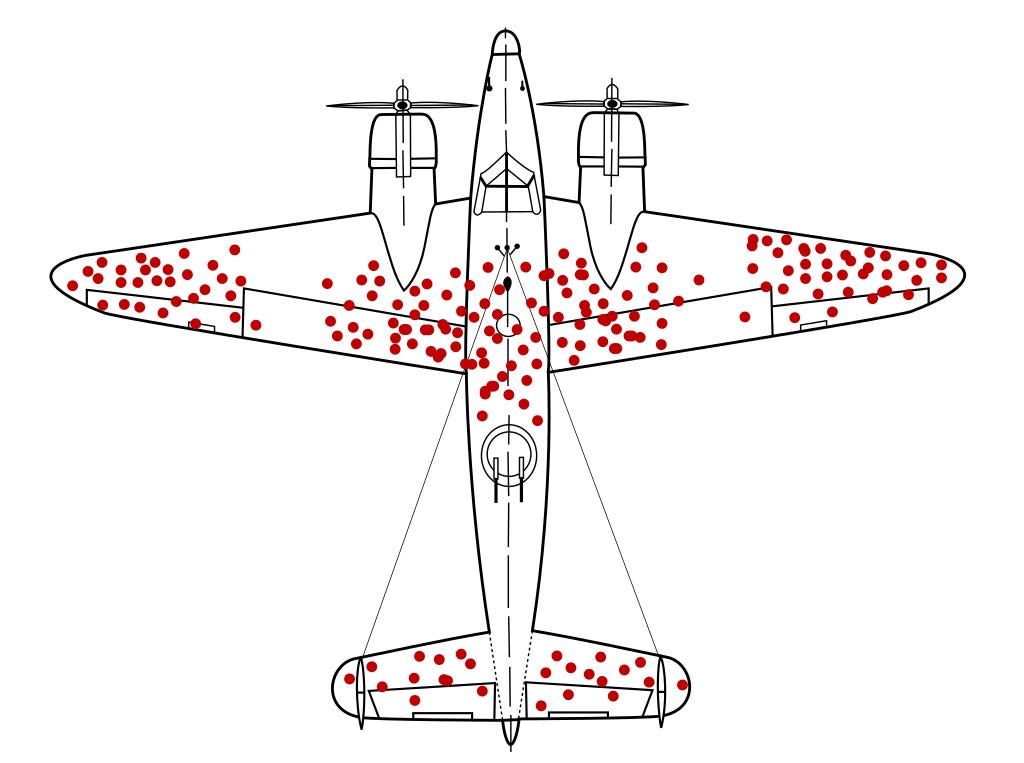
Many planes came back riddled with bullet holes in three main areas: the fuselage, the outer wings, and the tail. They came up with the solution to reinforce the hell out of the areas that had.
Survivorship Bias Free Stock Data Critical to Investors Kailash Concepts
World War II plane research: During World War II, statistician Abraham Wald and his research team at Columbia University encountered a fascinating example of survivorship bias in their study of bomber planes. Their task was to recommend areas for reinforcement on the aircraft based on an analysis of the damage sustained by returning planes.

Survivorship Bias Adam James
In statistics, survivorship bias can be defined as a form of sampling bias in which the observations taken at the end of a period of study do not conform to the random subset of the observations made at the beginning of the study.

There's This Thing Called "Survivorship Bias" Physiqonomics
The specific image of the "survivorship bias plane" comes from a Wikipedia editor McGeddon, and the photo is based on past work by Cameron Mill in 2005. As the creator of the original Wald diagram in 2005 that inspired the duplicates that have followed, absolutely yes.

Survivorship Bias Plane Exmplained Survivorship Bias Plane Know
Survivorship bias, or survivor bias, occurs when you tend to assess successful outcomes and disregard failures. This sampling bias paints a rosier picture of reality than is warranted by skewing the mean results upward. Survivorship bias is a sneaky problem that tends to slip into analyses unnoticed.

Survivorship Bias What World War II Taught Us About Our Mental Flaws
Wikipedia About Survivorship Bias Plane also known as Plane With Red Dots refers to a reaction image meme showing a diagram of a plane with red dots collected on its wings. The image is sourced from a Wikipedia page about survivorship bias, with World War II planes being used as an example of the concept.

Survivorship Bias 101 Black Belt in Thinking
Survivorship bias describes the error of looking only at subjects who've reached a certain point without considering the (often invisible) subjects who haven't. In the case of the US military they were only studying the planes which had returned to base following conflict i.e. the survivors.

Survivorship bias During WWII, the Navy tried to determine where they
1. Students design their own experiment/question to ask other students in school and see how many fall prey to survivorship bias. 2. Students choose a dream career and create an explanation for their parents as to why it is not an unrealistic dream, avoiding making arguments based on survivorship bias.
Grad School and Damaged Planes by Chad Orzel Counting Atoms
Survivorship bias is a form of selection bias. It occurs when a dataset only considers existing (or "surviving") observations and fails to consider observations that have ceased to exist.
Survivorship bias The Decision Lab
In finance, survivorship bias is the tendency for failed companies to be excluded from performance studies because they no longer exist. It often causes the results of studies to skew higher because only companies that were successful enough to survive until the end of the period are included.